The car oil system is an important part of your car to lubricate the engine, ensure the smooth running of the engine, and the life of all moving components of the engine engine oil pump Your car owes you a lot. Without it the engine would overheat or wear very quickly. But some may wonder: What is this, and why is it so important?
So now were now going through everything that you need to know about car engine oil pumps, from what they do and the different types, right through to the symptoms of a bad one.
What is a Car Engine Oil Pump?
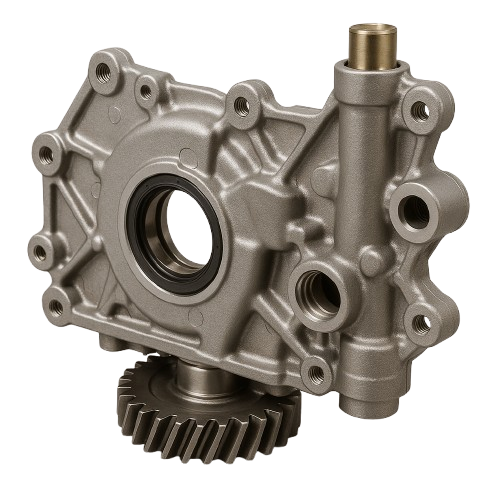
At its core, the car engine oil pump is responsible for circulating oil throughout the engine. This essential part ensures that all moving parts within the engine receive proper lubrication to minimize friction. The oil pump pulls oil from the oil pan and pushes it under pressure to the engine’s moving parts, including the crankshaft, camshaft, pistons, and valves. By reducing friction between these components, the oil helps prevent overheating and excessive wear.
The oil pump also helps in cooling the engine by dissipating heat that accumulates during combustion. Without adequate lubrication and cooling, parts of the engine could seize up or be damaged beyond repair. Hence, the oil pump is integral to maintaining engine health.
Types of Car Engine Oil Pumps
Several types of oil pumps are used in car engines, each with unique characteristics and advantages depending on the design and needs of the engine. Below are the most common types of car engine oil pumps:
1. Gear Oil Pump
This is the most common type of oil pump found in most car engines. The gear oil pump consists of two intermeshing gears that rotate, creating a suction force to pull the oil into the pump. As the gears turn, they pressurize the oil and push it into the engine’s oil channels. Gear oil pumps are reliable, cost-effective, and widely used due to their simple design and efficient performance.
2. Rotor (Rotary) Oil Pump
Rotor oil pumps operate using two rotors that turn within the pump housing, creating suction and pushing oil into the engine. These pumps are typically quieter than gear pumps and can handle a higher volume of oil, making them ideal for high-performance engines. While not as common in standard vehicles, rotor oil pumps are often found in sports cars and high-performance racing engines.
3. Crescent (Lobe) Oil Pump
The crescent oil pump uses two rotors that rotate within the pump housing, creating a crescent-shaped cavity. The oil is drawn into this cavity, and as the rotors turn, it forces the oil out into the engine. This type of pump is less common but can be found in some older or heavy-duty engines. Its design allows for higher oil pressure, which is beneficial for engines that experience higher stress and temperatures.
4. Vane Oil Pump
A vane oil pump operates using a series of sliding vanes that move within a chamber. As the vanes slide, they create suction, drawing oil into the pump. The oil is then pressurized and forced into the engine. Vane oil pumps are efficient and compact, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. While less commonly found in modern vehicles, they are still used in some specialty engines.
5. External Oil Pump
As the name suggests, an external oil pump is located outside the engine, typically mounted on the engine block. It works in the same manner as the internal oil pump but has the advantage of being easier to service or replace. External oil pumps are often found in heavy-duty or commercial vehicles, where high oil volumes and pressures are necessary.
Functions of the Car Engine Oil Pump
The engine oil pump does much more than just circulating oil. Let’s break down the various vital functions of this unassuming yet crucial component:
1. Lubrication
The most essential function of an oil pump is to ensure that all moving parts within the engine are properly lubricated. By delivering oil to parts like the crankshaft, camshaft, and pistons, the oil pump reduces friction, allowing these components to move smoothly. This lubrication prevents parts from grinding against each other, thereby reducing wear and tear on the engine.
2. Cooling
In addition to lubrication, engine oil also helps cool the engine. The oil absorbs heat generated during combustion and friction, helping to dissipate it and maintain optimal engine temperatures. The oil pump ensures that oil circulates properly to carry this heat away from critical engine components. Without adequate cooling, the engine could overheat and suffer serious damage.
3. Contaminant Removal
Oil also helps trap dirt, metal particles, and other contaminants that accumulate inside the engine. The oil pump ensures that oil flows through the oil filter, where these contaminants are removed before the oil is recirculated through the engine. This helps keep the engine clean and functioning optimally.
4. Pressure Regulation
Oil pressure is a critical factor in engine performance. If the pressure is too high or too low, the engine may suffer from poor lubrication, overheating, or damage. The oil pump ensures that the engine maintains the correct oil pressure by controlling the volume of oil that is pumped. Most oil pumps are designed to adjust the flow of oil according to the engine’s needs, ensuring proper lubrication under different operating conditions.
5. Sealing
Engine oil helps to create a seal between moving parts, preventing the loss of compression and reducing blow-by gases that can enter the crankcase. The oil pump plays a key role in ensuring that this seal is maintained by delivering sufficient oil to these areas.
Signs of a Failing Oil Pump
Knowing when your oil pump is starting to fail is crucial for preventing significant engine damage. Here are some common signs of a malfunctioning oil pump:
-
Low Oil Pressure: If the oil pump is failing, it may not be able to generate the required oil pressure, leading to a warning light on the dashboard.
-
Engine Noise: Lack of lubrication can result in engine components making unusual noises, such as knocking or grinding sounds.
-
Overheating Engine: Inadequate oil circulation can lead to engine overheating as the oil fails to carry away excess heat.
-
Oil Leaks: If the oil pump seals are damaged, it may cause oil to leak from the pump, leading to a noticeable loss of oil.
How to Maintain Your Oil Pump
Maintaining the oil pump is essential for prolonging the life of your engine. Here are some tips for keeping your oil pump in good condition:
-
Regular Oil Changes: One of the easiest ways to ensure your oil pump stays in good shape is to change the engine oil regularly. Clean oil allows the pump to work efficiently and reduces the risk of clogging.
-
Monitor Oil Levels: Keeping an eye on oil levels is critical. Low oil levels can strain the oil pump and lead to poor engine lubrication.
-
Check for Leaks: Oil leaks around the pump or oil pan should be addressed immediately, as they can lead to a loss of oil pressure and pump failure.
-
Use the Right Oil: Always use the recommended oil type and grade for your engine. Using the wrong oil can lead to poor pump performance and engine damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if the oil pump fails in a car?
If the oil pump fails, the engine will not receive adequate lubrication, leading to overheating, friction damage, and potentially total engine failure. If you notice oil pressure drops or engine noise, it’s crucial to address the issue immediately.
How long does an oil pump last?
The lifespan of an oil pump can vary depending on the vehicle and its usage. However, a well-maintained oil pump can last between 100,000 and 150,000 miles. Regular oil changes and proper maintenance can extend its life.
Can you drive with a bad oil pump?
It is not advisable to drive with a bad oil pump. Lack of proper lubrication can cause severe engine damage, which could lead to costly repairs or even engine replacement.
How do I know if my oil pump is working?
A healthy oil pump maintains proper oil pressure, ensures smooth engine operation, and prevents overheating. If your oil pressure light comes on, or if you hear engine knocking, it may indicate an issue with the pump.
What causes oil pump failure?
Common causes of oil pump failure include lack of maintenance, using the wrong oil, clogged oil passages, or worn-out pump components. Ensuring proper oil changes and using the right oil type can prevent premature failure.
Conclusion
The car engine oil pump is a vital component that ensures your engine runs smoothly by providing adequate lubrication and cooling. Understanding the types of oil pumps and their functions can help you maintain your vehicle better and avoid costly repairs. Regular maintenance, including timely oil changes and monitoring oil pressure, is essential for keeping your oil pump and engine in optimal condition. Always stay vigilant for signs of a failing oil pump, as timely intervention can save you from serious engine damage down the road.